Backup & Restore Stateless Workloads with Velero for Kubernetes

This article is part of a series of blog posts on using Velero for Kubernetes backup, restore, migration & disaster recovery.
All articles in this series explore Velero in the context of AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS).
Stay tuned as we publish more articles in the coming weeks & months. Here’s a sneak preview of what’s to come:
- An Introduction to Velero for Kubernetes Backup & Restore
- Velero for Kubernetes Backup: Install & Configure
- Backup & Restore Stateless Workloads with Velero for Kubernetes
- Velero for Kubernetes: Backup & Restore Stateful Workloads with AWS EBS Snapshots
- Velero for Kubernetes: Backup & Restore Stateful Workloads with Restic for Velero
- Monitoring Velero Kubernetes Backups & Automated Alerting for Backup Failures
Introduction
In this post, we will backup & restore a simple stateless Nginx workload.
You can back up or restore all objects in your cluster, or you can filter objects by type, namespace, and/or label.
All backups have a default TTL of 720 hours (30 days), and can be set to never expire.
Install Nginx
We will be using Bitnami’s Nginx Helm chart to create a Nginx workload in our cluster.
First add the Bitnami Helm repo:
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnamiNow install Nginx as follows:
helm install nginx bitnami/nginx \
--namespace nginx --create-namespace Wait for it to come up:
> kubectl get all --namespace nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-86f4b77fb8-mxd27 1/1 Running 0 101s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx LoadBalancer 10.100.188.63 adf40b6d4fc0047198fc8220eb97f90d-1730345072.ap-south-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:32610/TCP 101s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx 1/1 1 1 101s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/nginx-86f4b77fb8 1 1 1 101sEnsure the Nginx load balancer was created in AWS:
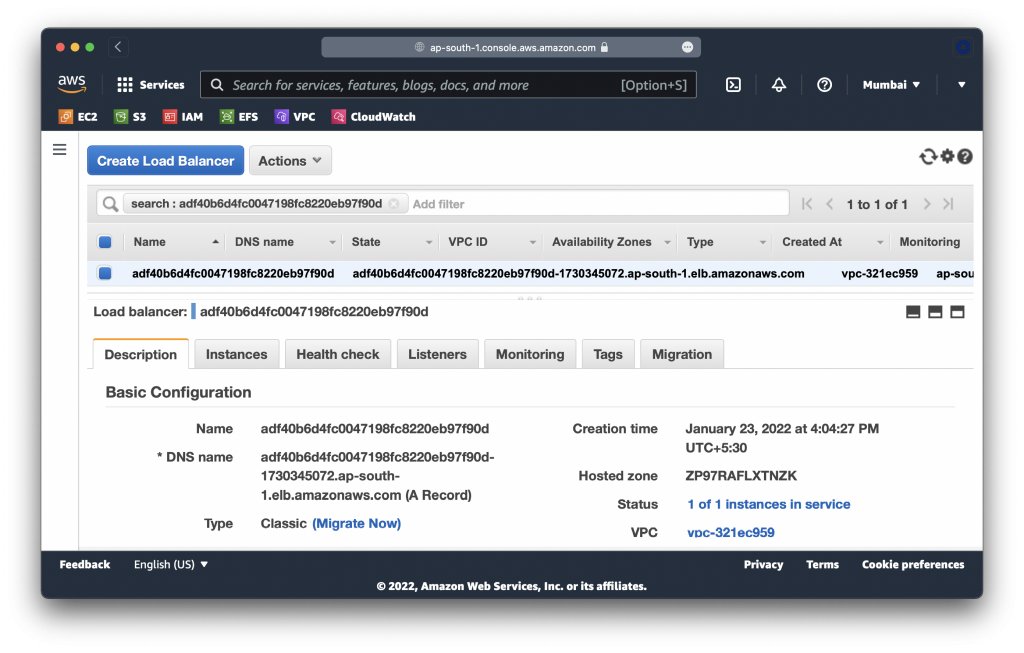
You can also visit the load balancer URL in your browser to ensure Nginx is up.
Backup Nginx
Backing up the Nginx namespace is as easy as:
> velero backup create nginx --include-namespaces nginx
Backup request "nginx" submitted successfully.
Run `velero backup describe nginx` or
`velero backup logs nginx` for more details.Check the status of the backup:
> velero backup describe nginx
Name: nginx
Namespace: velero
Labels: velero.io/storage-location=default
Annotations: velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-gitversion=v1.21.5-eks-bc4871b
velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-major-version=1
velero.io/source-cluster-k8s-minor-version=21+
Phase: Completed
Errors: 0
Warnings: 0
Namespaces:
Included: nginx
Excluded: <none>
Resources:
Included: *
Excluded: <none>
Cluster-scoped: auto
Label selector: <none>
Storage Location: default
Velero-Native Snapshot PVs: auto
TTL: 720h0m0s
Hooks: <none>
Backup Format Version: 1.1.0
Started: 2022-01-22 19:12:30 +0530 IST
Completed: 2022-01-22 19:12:32 +0530 IST
Expiration: 2022-02-21 19:12:30 +0530 IST
Total items to be backed up: 20
Items backed up: 20
Velero-Native Snapshots: <none included>Delete Nginx
Now let’s simulate the loss of our workload:
> kubectl delete namespace nginx
namespace "nginx" deletedWait for the namespace to be gone:
> kubectl get namespaces
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 10d
kube-node-lease Active 10d
kube-public Active 10d
kube-system Active 10d
velero Active 22hNotice that the load balancer is also gone:
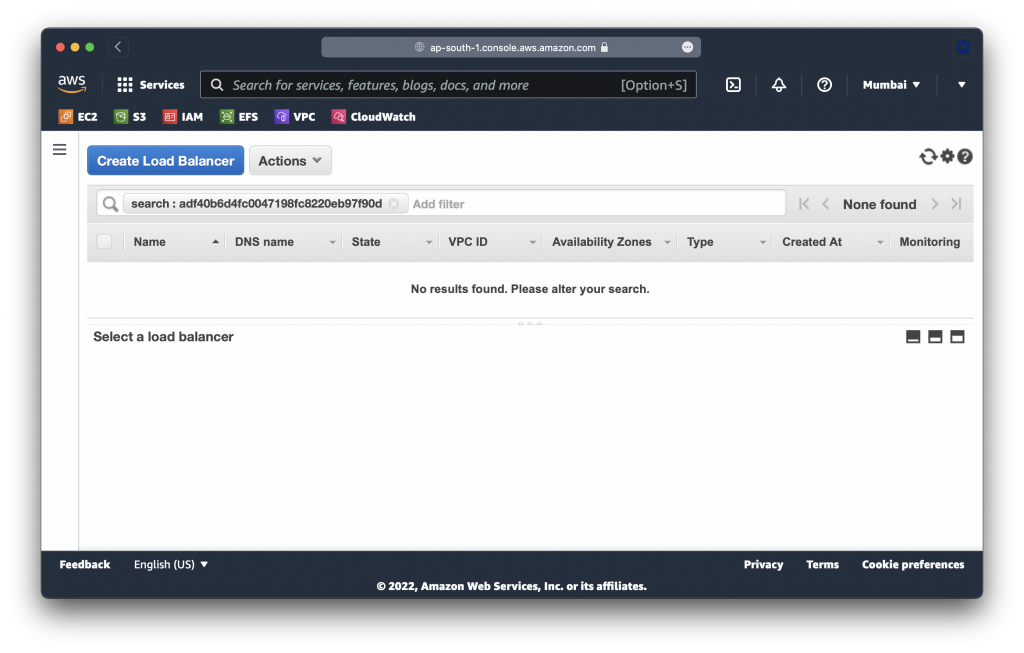
Restore Nginx
Now, let’s try to restore the entire namespace to its former glory:
> velero restore create nginx --from-backup nginx
Restore request "nginx" submitted successfully.
Run `velero restore describe nginx` or
`velero restore logs nginx` for more details.Check up on the status of the restore:
> velero restore describe nginx
Name: nginx
Namespace: velero
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Phase: Completed
Total items to be restored: 12
Items restored: 12
Started: 2022-01-23 16:20:02 +0530 IST
Completed: 2022-01-23 16:20:03 +0530 IST
Backup: nginx
Namespaces:
Included: all namespaces found in the backup
Excluded: <none>
Resources:
Included: *
Excluded: nodes, events, events.events.k8s.io, backups.velero.io, restores.velero.io, resticrepositories.velero.io
Cluster-scoped: auto
Namespace mappings: <none>
Label selector: <none>
Restore PVs: auto
Preserve Service NodePorts: autoLet’s see if our workload is back:
> kubectl get namespaces
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 10d
kube-node-lease Active 10d
kube-public Active 10d
kube-system Active 10d
nginx Active 2m11s
velero Active 22h> kubectl get all --namespace nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/nginx-86f4b77fb8-v67gc 1/1 Running 0 2m21s
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/nginx LoadBalancer 10.100.185.209 ac48b1eab10f0458cb671a947c819715-1827482840.ap-south-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:30012/TCP 2m21s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/nginx 1/1 1 1 2m21s
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/nginx-86f4b77fb8 1 1 1 2m21sNotice that a new load balancer was provisioned:
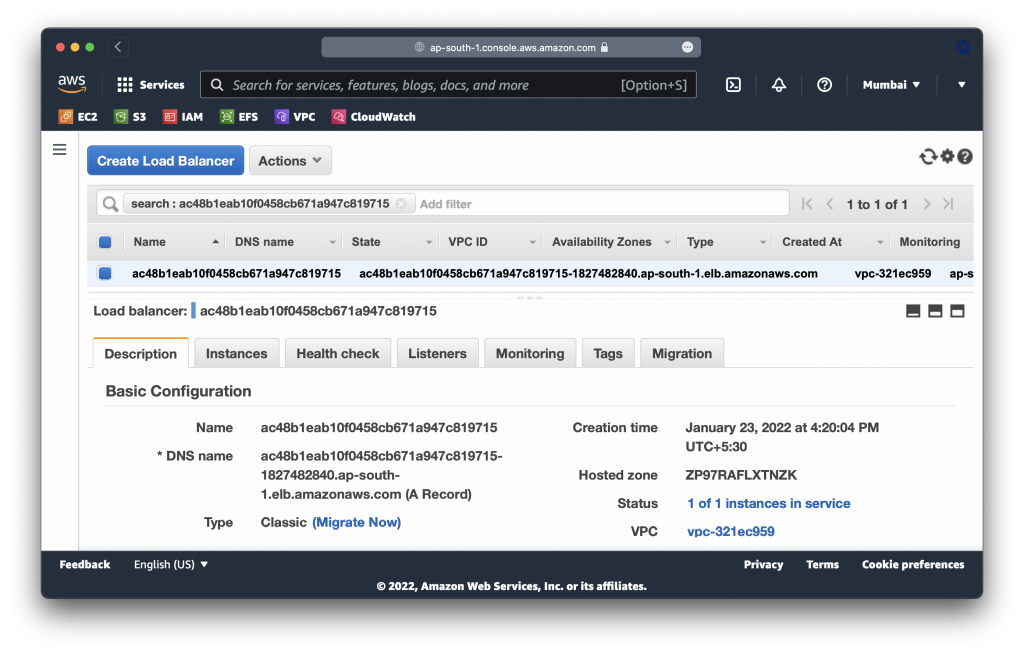
Give it a minute & you’ll be able to see the Nginx homepage at the load balancer’s URL too.
Backup Scenarios
So far, we’ve only backed up & restored an entire namespace. You can do the same for:
Resources with a label:
velero backup create nginx --selector app=nginxOr scheduled backups:
velero schedule create nginx-daily \
--schedule="0 1 * * *" \
--include-namespaces nginxFinally, backups can be deleted by:
velero backup delete nginxThis deletes the backed up files in S3 & the instance of Velero’s “backup” CRD from the cluster.
Backups in S3
The contents of the S3 bucket after a backup & restore are:
S3 bucket
├── backups
│ └── nginx-backup (backup name)
│ ├── nginx-backup-csi-volumesnapshotcontents.json.gz
│ ├── nginx-backup-csi-volumesnapshots.json.gz
│ ├── nginx-backup-logs.gz
│ ├── nginx-backup-podvolumebackups.json.gz
│ ├── nginx-backup-resource-list.json.gz
│ ├── nginx-backup-volumesnapshots.json.gz
│ ├── nginx-backup.tar.gz
│ │ ├── configmaps
│ │ │ ├── namespaces
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ │ └── kube-root-ca.crt.json
│ │ │ └── v1-preferredversion
│ │ │ └── namespaces
│ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ └── kube-root-ca.crt.json
│ │ ├── deployments.apps
│ │ │ ├── namespaces
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-deployment.json
│ │ │ └── v1-preferredversion
│ │ │ └── namespaces
│ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ └── nginx-deployment.json
│ │ ├── endpoints
│ │ │ ├── namespaces
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ │ └── my-nginx.json
│ │ │ └── v1-preferredversion
│ │ │ └── namespaces
│ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ └── my-nginx.json
│ │ ├── endpointslices.discovery.k8s.io
│ │ │ ├── namespaces
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ │ └── my-nginx-hjmpg.json
│ │ │ └── v1-preferredversion
│ │ │ └── namespaces
│ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ └── my-nginx-hjmpg.json
│ │ ├── events
│ │ │ ├── namespaces
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ │ └── my-nginx.16c998feece6df20.json
│ │ │ └── v1-preferredversion
│ │ │ └── namespaces
│ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ └── my-nginx.16c998feece6df20.json
│ │ ├── namespaces
│ │ │ ├── cluster
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-example.json
│ │ │ └── v1-preferredversion
│ │ │ └── cluster
│ │ │ └── nginx-example.json
│ │ ├── pods
│ │ │ ├── namespaces
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ │ ├── nginx-deployment-57d5dcb68-9n4qh.json
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-deployment-57d5dcb68-fhdbh.json
│ │ │ └── v1-preferredversion
│ │ │ └── namespaces
│ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ ├── nginx-deployment-57d5dcb68-9n4qh.json
│ │ │ └── nginx-deployment-57d5dcb68-fhdbh.json
│ │ ├── replicasets.apps
│ │ │ ├── namespaces
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-deployment-57d5dcb68.json
│ │ │ └── v1-preferredversion
│ │ │ └── namespaces
│ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ └── nginx-deployment-57d5dcb68.json
│ │ ├── secrets
│ │ │ ├── namespaces
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ │ └── default-token-kcmks.json
│ │ │ └── v1-preferredversion
│ │ │ └── namespaces
│ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ └── default-token-kcmks.json
│ │ ├── serviceaccounts
│ │ │ ├── namespaces
│ │ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ │ └── default.json
│ │ │ └── v1-preferredversion
│ │ │ └── namespaces
│ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ └── default.json
│ │ └── services
│ │ ├── namespaces
│ │ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ │ └── my-nginx.json
│ │ └── v1-preferredversion
│ │ └── namespaces
│ │ └── nginx-example
│ │ └── my-nginx.json
│ └── velero-backup.json (metadata)
└── restores
└── nginx-backup-TIMESTAMP
├── restore-nginx-backup-TIMESTAMP-logs.gz
└── restore-nginx-backup-TIMESTAMP-results.gzConclusion
In this post, we tried our hands on a real backup & restore scenario for a stateless workload.
In the next post, we will try backing up a stateful WordPress workload.
About the Author ✍?

Harish KM is a Principal DevOps Engineer at QloudX. ???
With over a decade of industry experience as everything from a full-stack engineer to a cloud architect, Harish has built many world-class solutions for clients around the world! ??♂️
With over 20 certifications in cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP), containers (Kubernetes, Docker) & DevOps (Terraform, Ansible, Jenkins), Harish is an expert in a multitude of technologies. ?
These days, his focus is on the fascinating world of DevOps & how it can transform the way we do things! ?





