Using Amazon API Gateway to route requests to RESTful micro services in Amazon ECS
This article is in continuation to an earlier article where we deployed RESTful microservices as Docker containers in Amazon ECS. There we used path-based routing configured in an internet-facing ALB, to invoke the REST APIs from outside AWS. But since these are just REST APIs, the ideal way to set them up would be using Amazon API Gateway!
API Gateway provides us numerous features which our ALB can’t:
- Authentication & authorization.
- Throttling.
- Caching responses.
- API lifecycle management: dev, QA, prod.
- SDK generation.
- API operations monitoring: API calls, latency & error rates.
- CloudWatch alarms for abnormal API behaviors.
- API keys for 3rd-party developers.
Let’s get started. Here’s what we’ll set up:
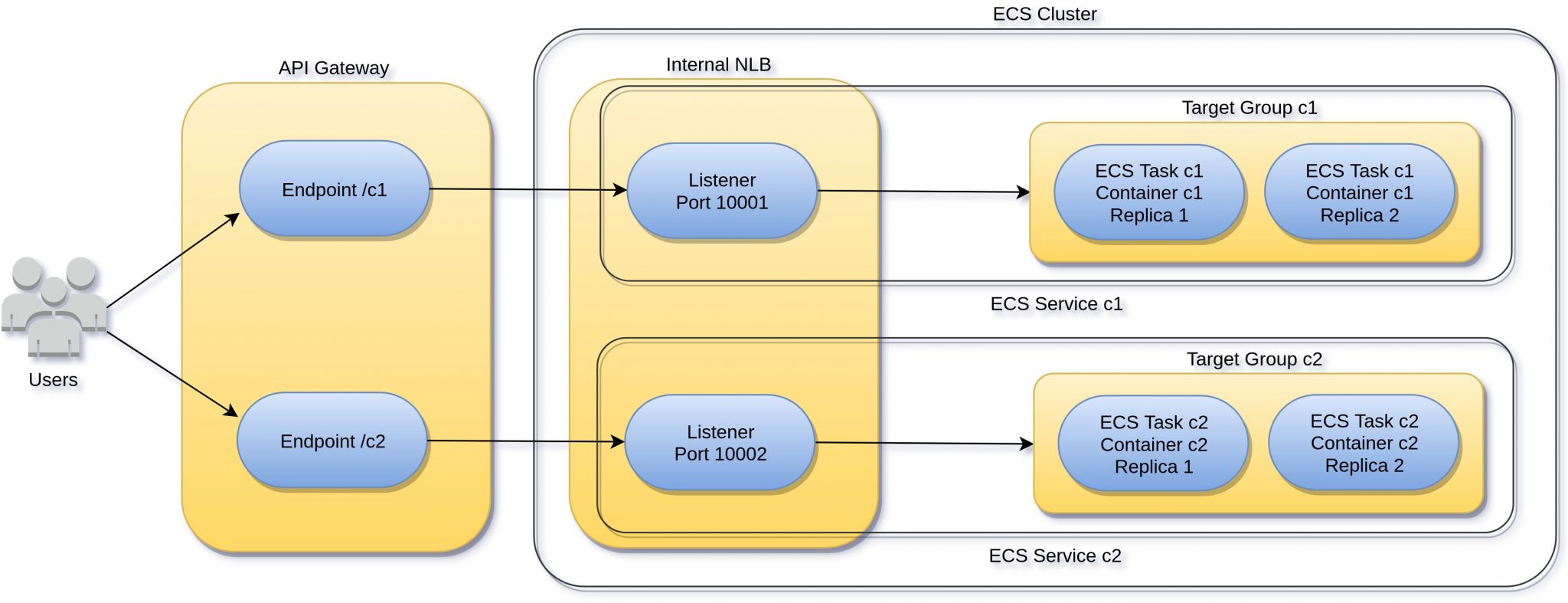
Follow the steps here to create the ECS task definitions & cluster. Next, create an internal Network Load Balancer (NLB):
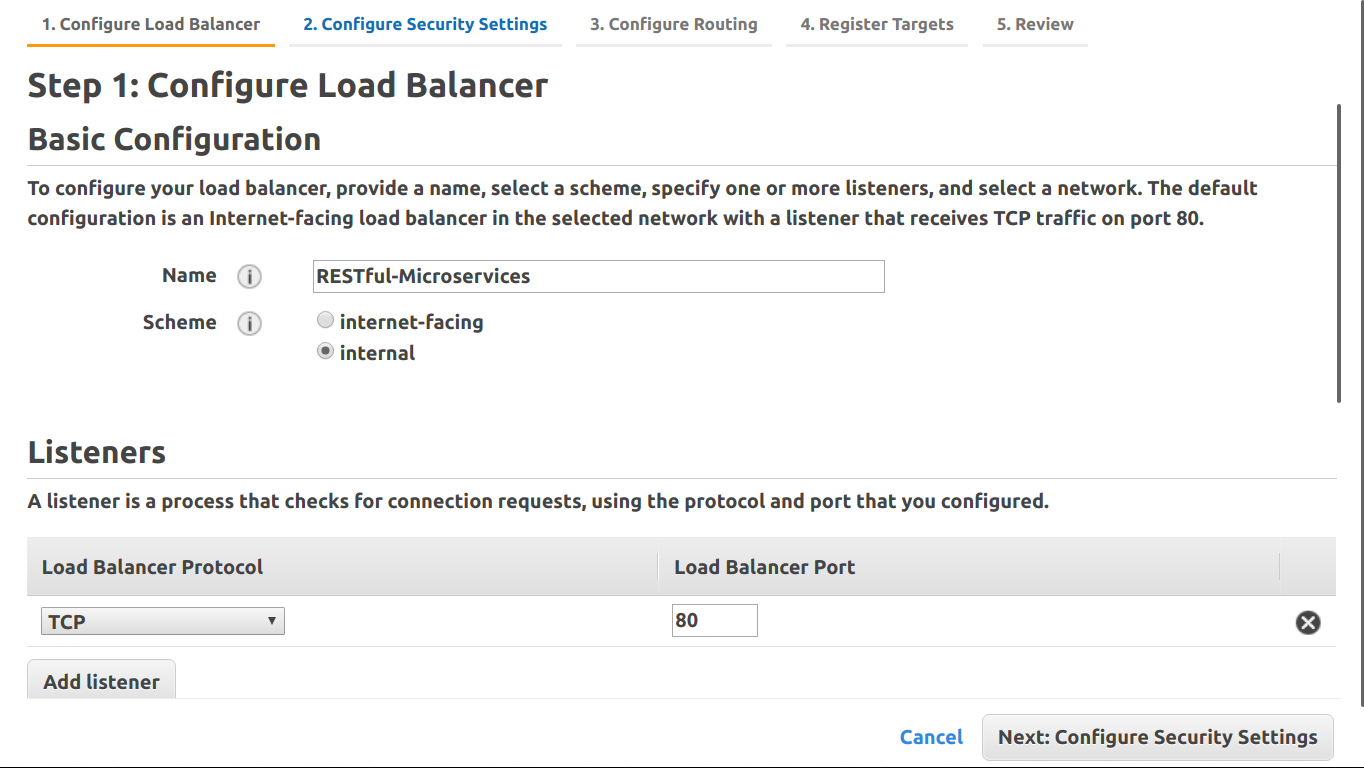
We won’t be using the default listener but you’ll have to leave it in there or the wizard won’t let you proceed. Select VPC & one public subnet per AZ & move on to the next step. Create or select security group(s) & target group & finish creating the LB.
Follow the steps here to begin creating the ECS service up to the point of LB selection. There, select NLB instead of ALB & add a container to LB as shown here:
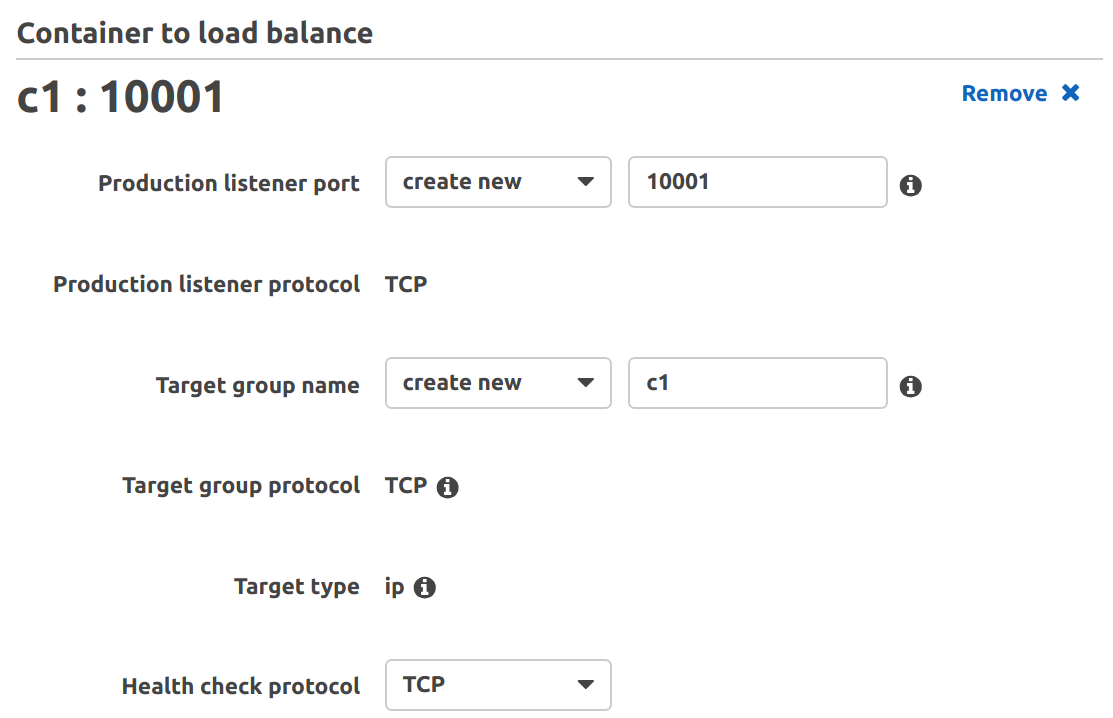
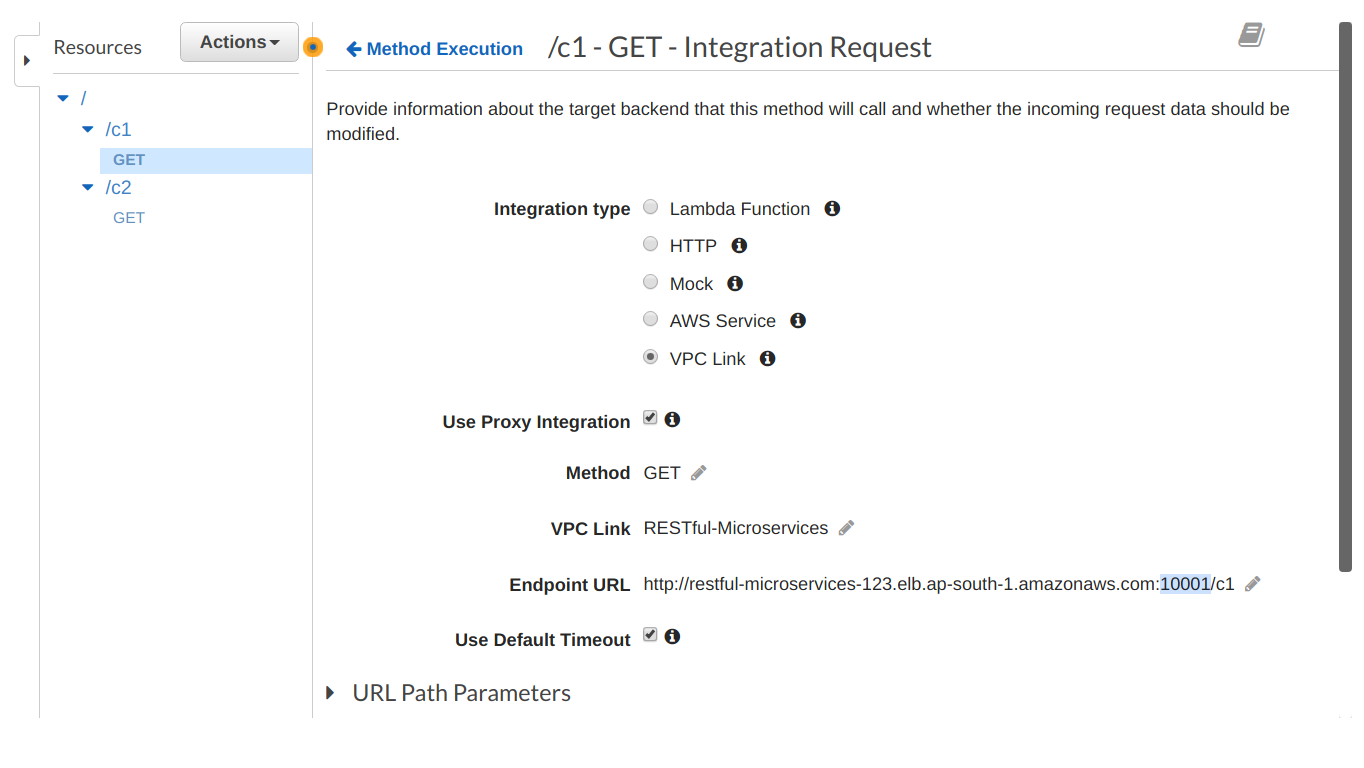
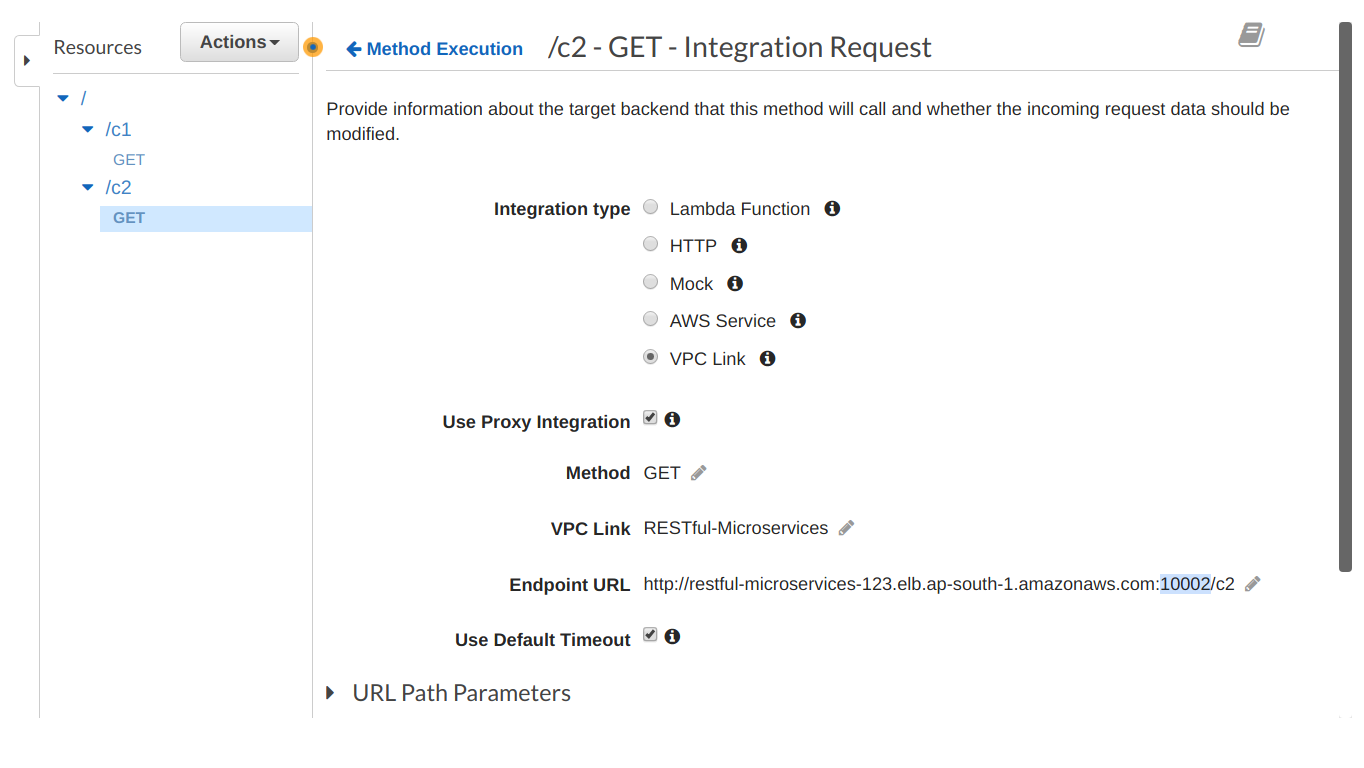
Finish creating the ECS service. Next, we create the API Gateway resources. In order to route requests hitting the API Gateway, to our internal NLB, we’ll need to create a VPC link. Follow the steps outlined here to create a VPC link to our NLB & use it as an integration type with all API methods. Note that since we’re using NLB, we’ll need a different port listener for each container, such that each API method points to a different port of the same NLB:
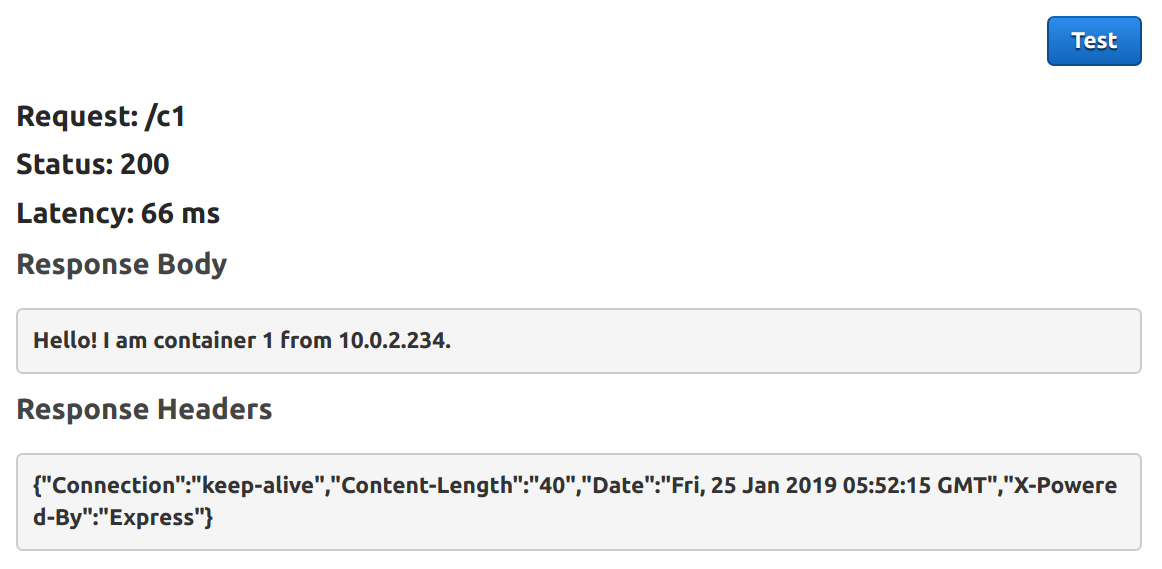
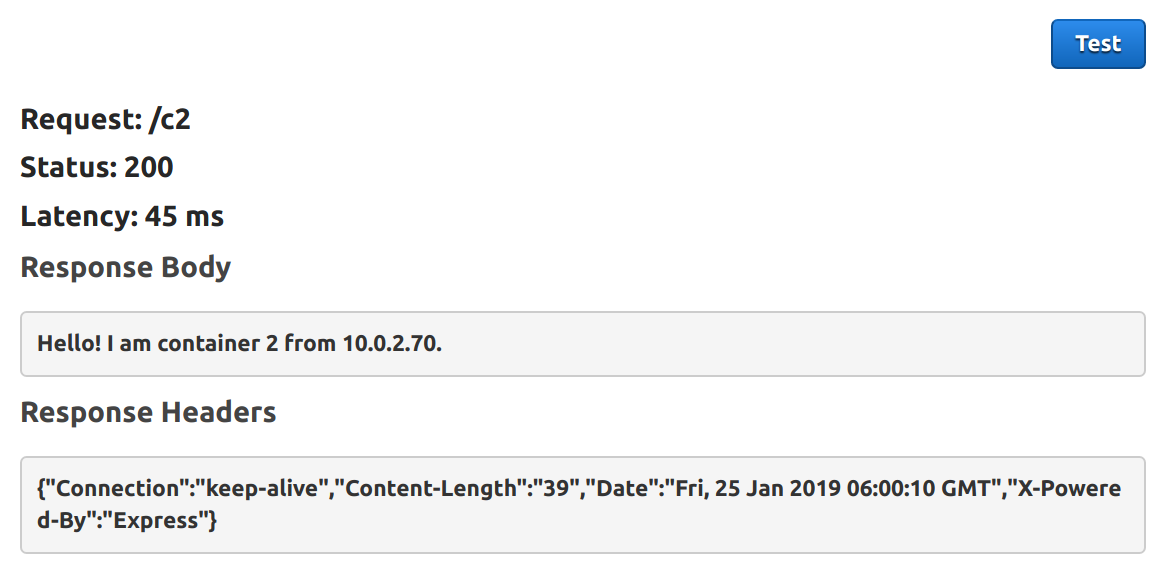
Testing the APIs now should get us the expected response:
Anand is the Cloud Innovation Head & Delivery Manager at QloudX and he passionately pursues cloud nirvana.





